How can we help you?
Find an answer to your questions concerning data recovery with Recovery Explorer in the list below. If it’s not there, feel free to contact us.
List of frequently asked questions about data recovery
How should I install the program?
Download the software by pressing the Download button from the web site. Remember to avoid using the disk you lost your data from as a target location for saving the app! After the download is finished, you get an executable file with the icon of a Software Manager application which can be run in your operating system. Go to Setup instructions to learn more about the peculiarities of installing the program on Windows, macOS and Linux.
How can I switch to the wizard-based mode?
If you want to recover your files in a simplified Wizard-based mode, switch to it by pressing Recover data in Wizard mode in the lower left corner of the application tab.
What are the limitations of the trial version?
Recovery Explorer is shareware software. All its functions are available in the trial version and you can try them out before actually buying the program. Still, this version has its limitations on saving files. Recovery Explorer Standard does not save recovered files that are bigger than 256 KB. Recovery Explorer RAID does not save recovered files that are bigger than 768 KB. Recovery Explorer Professional does not save recovered files that are bigger than 768 KB. If Recovery Explorer managed to find your files and fits your purposes, purchase the software license to continue the data recovery procedure.
Why is the size of my disk displayed incorrectly?
The problem may lie in the connection of the storage. A bridge chip of the adaptor may be incapable of transferring data located at large addresses because of its data transmission ability. That’s why disk sizes displayed in Recovery Explorer can differ from the real ones. The same problem may also arise for internal drives in case of a poor bandwidth of an old motherboard.
How should I choose the right storage?
Recovery Explorer automatically detects and displays all devices attached to the local computer. To start data recovery, you need to decide on a logical volume or a physical storage. The only file system of a storage is displayed as the only logical volume, if it is defined as a logical disk under Windows or if it is a LVM volume under Linux. At the very first tab, the program shows logical volumes of all data storages giving a summary of their properties – the label and name of the volume, the title of the file system as well as the size of the disk volume. At the same time, don’t be afraid of making a wrong choice: you will be able to select any other storage later at each of the further steps.
Why is the network disk missing from the list?
A Network Attached Storage is a stand-alone data storing and sharing device which uses certain software protocols to establish communication with your computer. These protocols are aimed at file access rather than at data recovery functions. For this reason, before starting data recovery from a NAS, you need to take all the NAS disks out of the box and connect them to the local computer for recovery.
Why is my disk missing from the list?
If Recovery Explorer doesn’t display a physical disk, check if this disk is attached properly to your computer. Doing so, examine whether the data connector and the power supply cable are connected firmly to the hard drive and have no breaks. Make sure that the driver software is properly installed for both the adapter device and the disk device itself. Yet, if everything seems to be in order, but the disk is still not displayed, your drive can have physical damages and you should turn to a data recovery center. If Recovery Explorer doesn’t display a USB-drive, press Refresh drives to update the information about the newly connected storages. Use this button for every new connection. If this doesn’t solve the problem, a broken USB slot may be the issue. Try a neighboring USB slot. If the problem remains, there may be issues with the USB storage itself. In such a case turn to a data recovery center.
How should I choose the right partition?
If the physical drive is divided into several logical partitions, Recovery Explorer displays these partitions as storage subdivisions with the details about their properties. By clicking on a storage partition you can find the summary on partition properties – the type of the file system, its size, the start sector of the partition as well as its condition. Select the one matching your criteria and start the scanning operation. If you cannot find the partition which was affected by data loss or if it seems damaged, press Ignore these partitions at the bottom to start complete disk scan.
Where can I find the recovered files?
Basically, Recovery Explorer completely repeats the structure of the data source. For this reason, you can easily find them among the files and folders displayed in the explorer. Another way to find files easily is to use the quick search box. Enter the name of the file or its extension into the search line and press the Search button or Enter. The software will find the requested files and sort them into specially created folders.
What is the $Lostfiles folder?
Recovery Explorer virtually builds the initial structure of the file system of the source storage addressing all found files to their native folders. If for some reason a native folder has undergone irreversible changes that made it unrecoverable, the program will sort such a file to the special $LostFiles folder. Thus, if you cannot find your file at its regular place, you can still look for it in the $LostFiles folder.
Why do some file names consist of numbers?
The result and quality of data recovery depend heavily on the file system that manages files on your disk. Although some file systems keep the file names after the deletion operation, some of them tend to erase file names. If the name of a file is lost, Recovery Explorer will find and recover such a file by using the same data recovery criteria but without its name. At the same time, it assigns a certain number to its name. Use the program's viewing tool to check if it is the file you would like to retrieve.
Why is my target storage missing from the list?
The software hides the source storage medium to prevent data overwriting, which leads to irreversible loss of your files. Chose another location and continue. If you are sure that this is not the source storage, examine all the storage connections first. In case of an external device, press Refresh storages for the software to update the information about newly attached devices.
How can I use my network storage as a target storage?
Windows OS, without UAC
To make the storage directly available among the target storages, map the network location to the local logical disk.
Windows OS with UAC
To make the network storage available under the privileged user account context, map the network storage with Reconnect at log-on:
Setting in Windows:
Go to This computer context menu;
Select Map network drive;
Select the drive and tick Reconnect at the log-on checkbox;
Copy the full drive path using the address bar;
Settings in Recovery Explorer:
Press Other locations (advanced) in the target selection dialog;
Select an “offline” network storage for target location.
After the first access, the network location turns to the “online” status and becomes available in the target locations. As an alternative, a direct path can be used:
Navigate to the destination network folder using the Network location in File Explorer;
Copy the network location path in the address bar of File Explorer;
In Recovery Explorer, press Other locations (in the advanced mode) in the target selection dialog;
Insert the storage path into the program address box;
Press Select.
Now the network target storage is available for saving recovered files.
To learn more about working with network attached storages and saving recovered files to them in other operating systems (including Linux and macOS), go to.
What do target storage colors mean?
Recovery Explorer marks target storages with colors to help you easily find the proper one to save your recovered files to.
Storages marked:
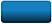 - blue have no limitations on saving the files you have selected for recovery;
- blue have no limitations on saving the files you have selected for recovery; - violet are capable of storing each of the files but don’t have enough capacity to place them all;
- violet are capable of storing each of the files but don’t have enough capacity to place them all; - gray may not allocate some of the selected files.
- gray may not allocate some of the selected files.
You can still try saving files separately though.
Why do recovery errors occur?
Failures during the process of copying files might occur for various reasons:
Trial license limitations. Buy the software license to remove all trial version limitations and continue recovering your files.
Problems with disk reading. Create a disk image and retry the entire recovery process from the image.
Incorrect disk size detection. Check the disk size and change the disk adapter if the size is detected incorrectly.
Disk is part of a RAID. Retry the recovery selecting the storage from the Complex (RAID) storages tab.
If Recovery Explorer doesn’t assemble your RAID, use a data recovery software with the RAID assembly function.
Severe file system damage. Try looking for your files in the folders Found files and Extra found files.
What if some files are missing?
If you cannot find your files at the very last step of the recovery process with Recovery Explorer, examine the recovery result once again. You may also try searching them in the $LostFiles, Found files and Extra found files folders.