The most common reasons for data loss
Despite apparent reliability of modern computers, users still lose their crucial information. Even expensive high-quality hardware equipment and utterly reliable software cannot guarantee 100% failure resistance of your PC or laptop.
Data loss can be defined as inability to access data at its usual place by usual program means due to errors in software/hardware operation or due to user's improper actions.
Failures that lead to data loss are generally divided into two categories: physical and logical. A physical failure is caused by the problems with any physical component of the computer, whereas a logical failure is related to the issues with its logical structure.
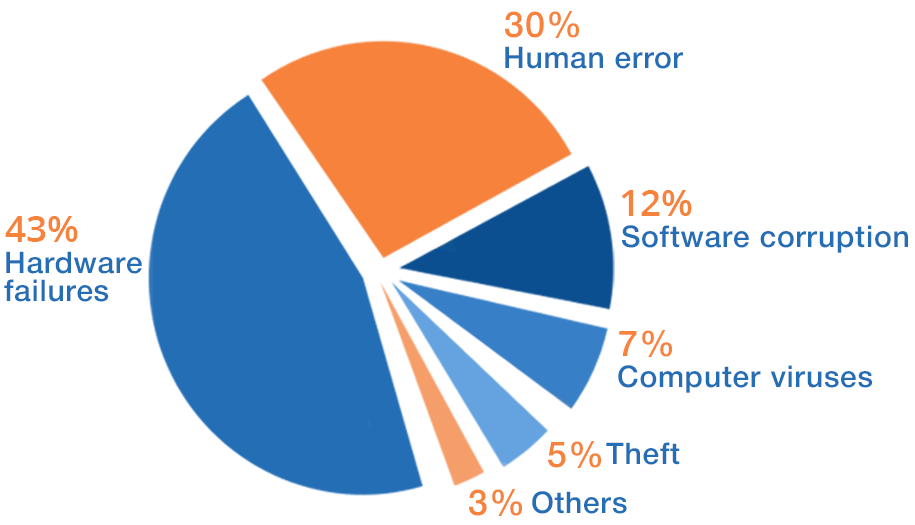
The pie chart above illustrates the percentage ratio of common data loss causes.
Hardware failures

Hardware failures with 42% of occurrence frequency take the first place among the most widespread causes of data loss. These include issues with the following components of the computer system:
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) / Solid State Drive (SSD);
Computer memory (RAM);
Motherboard;
Processor (CPU);
Power supply (PSU).
The breakdown of a disk storage which physically stores the data is likely to result in data loss. As soon as you detect a HDD/SSD failure, under no circumstances should you disassemble the storage, provided that you are not a data recovery professional.
Human errors
Mistakes made by computer users or operators due to either lack of experience or inattentiveness take the second place after hardware failures. Human errors become the reason for data loss in 30% of cases, proving once again that even Homer nods.
Accidental deletion of important files
When working with files, users may accidentally delete some important data. The operating system offers two alternative ways of performing the file deletion procedure: Files can be deleted with the help of the Recycle Bin, which is a two-step method – first, you delete a file using a context menu or pressing the “Delete” button on the keyboard, second, you empty the Recycle Bin. Another way to delete a file is to press Shift + Delete keys – it will immediately be removed bypassing the Recycle Bin. Certainly, the OS will warn the user of possibly erroneous actions, but, as a rule, users fail to pay attention to the warning messages.
Negligent disk or disk partition formatting without a backup copy
It goes without saying that one must make a backup copy of all the important files before formatting the drive, but mistakes are sometimes bound to happen. Also, when deciding to reinstall the operating system, the user may accidentally select the wrong partition and find that out when the installation is already in progress.
Overwriting of file contents
Any file editor, whether document, video, image, picture or audio, enables the user to alter the contents of the file. Once the “Save” button is pressed and the file is closed, new contents are written over the former ones. Unfortunately, if for some reason you need the previous version of the file, this case cannot be handled by any data recovery software. The only thing you can do is to recreate the file from scratch.
Inaccurate attempts to recover the lost information
Having realized that the data is lost, it is important to refrain from all slapdash actions which may lead to irreversible data loss. Don’t use any system repair tools such as CHKDSK. These utilities usually try filling in the missing information on the disk, causing hazardous data overwriting. CHKDSK can also misunderstand the file system problem and do an inappropriate repair.
Software crashes
With 13% of frequency, software malfunctions take the third place in the list of data loss causes. According to the data recovery experts from SysDev Laboratories, the main types of software corruption are the following:
Backup software. An error may happen during the process of backing up files. The file copies may appear to have failed to be created meanwhile the files have already been deleted.
File editors. A file editing software failure may cause file corruption. Another common reason is a failure during the procedure of saving files in bulk, when some of the files are updated to the latest modifications but the rest are damaged.
Antivirus software. An antivirus program may consider the “good” files to be malware and delete them.
Converters. An error may occur during the process of changing the file format.
Computer viruses
 Like an ordinary virus intrudes on a live organism, a computer virus intrudes on the computer system with the aim to modify the way it operates. It is important to know that computer viruses, first of all, may damage or delete any data on the computer without the user's consent, and, secondly, they are able to spread, infecting other devices. Although computer viruses become the reason for data loss only in 7% of cases, they may bring about serious trouble.
Like an ordinary virus intrudes on a live organism, a computer virus intrudes on the computer system with the aim to modify the way it operates. It is important to know that computer viruses, first of all, may damage or delete any data on the computer without the user's consent, and, secondly, they are able to spread, infecting other devices. Although computer viruses become the reason for data loss only in 7% of cases, they may bring about serious trouble.
Computer viruses are small computer programs. However, unlike normal software, they cannot be controlled and their actions are targeted against the user. The factors causing virus attacks include:
downloading cracked and pirate software;
opening attachments from unfamiliar e-mail addresses;
surfing unreliable web-sites;
non-use of anti-virus programs.
Data recovery specialists at SysDev Laboratories recognize more than twenty different types of malware, emphasizing the crypto virus as the most severe and troublesome. The crypto virus, also known as ransomware, encrypts the existing files on the affected machine using RSA public-key cryptography, with the private key stored only on the malware's control servers. Then the hackers ask their victim to pay a ransom to get the encryption key. They also set a deadline, and if it is broken, the files get deleted or the victim has to pay even a higher price. Presently, there doesn’t exist a way to break ransomware if it has already managed to affect your device. The only viable solution is timely and systematic backups.
Theft

A low rate of 5% of cases is related to data theft. Leaving out the cases of data theft when a physical device gets stolen, there are also a lot of instances of logical robbery.
The intruders aim to get the most of the user's financial and confidential information. As a rule, their target is customer databases of private companies and healthcare establishments, banking details, passwords, secret private or corporate information.
Logical data theft is usually beyond the area of expertise of data recovery companies. However, they may make a forensic inspection of the computer to trace the evidence of breach.
Protection against data theft is rather an issue of precaution and not post factum actions. Commonly known means are using antivirus programs, encryption, employment of secured data management systems, using passwords and laptop lockdowns such as Kensington key.
Other causes

The remaining 3% include mainly the impacts of natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and fires. They strike rarely, but right on target!
Catastrophes cause physical computer damages. Not only data storage media but other components of the computer system can be broken, whereas the storage itself may still remain intact. This is good news for users who do not want to turn to a data recovery center. And yet, if you discover that the trouble is in the data storage itself, never try to get inside of it unless you are a data recovery specialist.
Unfortunately, the nature neither steps back in its plans nor informs about them. The most reasonable piece of advice is to make timely and preferably off-site backups. Cloud solutions are probably the best option in this case.
Conclusion
Every PC user is at the potential risk of losing precious information. Whatever the real cause of your exact data loss case is, there is always a solution. Deleted files aren't really wiped until something is written over them, so if you act immediately, you can get them back. In case of a physical damage, turn to a data recovery center. In case of a logical failure, be sure to have comprehensive data recovery software at your disposal to bring your files back to the normal state.